This video teaches how to use calculus find the position, velocity and acceleration of an object. Imagine an object moving on a straight line. It's position at any time (t) is given as s(t) pronounced "s of t". It's velocity is v(t)= s'(t) which is the derivative of s(t). It's acceleration a(t) is the derivative of its velocity v'(t). If we look at it from a different perspective we are differentiating. The derivative of the position is its velocity, the derivative of its velocity is it acceleration, etc. To go in the opposite direction we have to anti-differentiate. An example problem would be: An object is moving along a straight line with an acceleration of a(t)= 12t-6 ft/sec squared. If v(1)=9 ft/sec and s(1)=15 ft , find v(t) and s(t). He will solve the problem in a future video.
Apple's iOS 26 and iPadOS 26 updates are packed with new features, and you can try them before almost everyone else. First, check Gadget Hacks' list of supported iPhone and iPad models, then follow the step-by-step guide to install the iOS/iPadOS 26 beta — no paid developer account required.




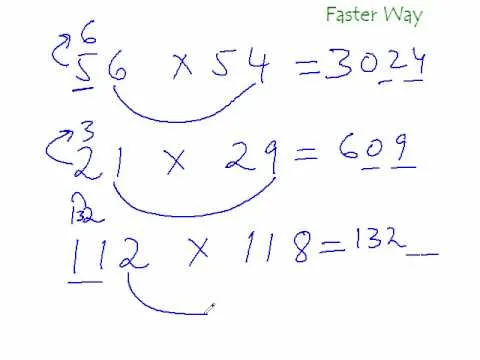
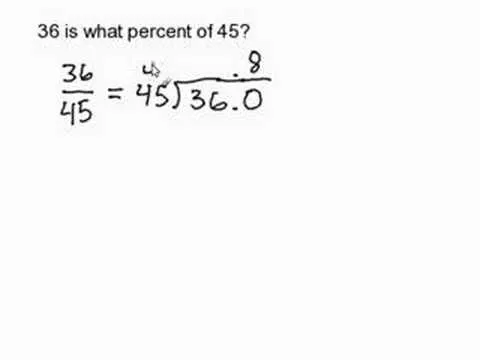
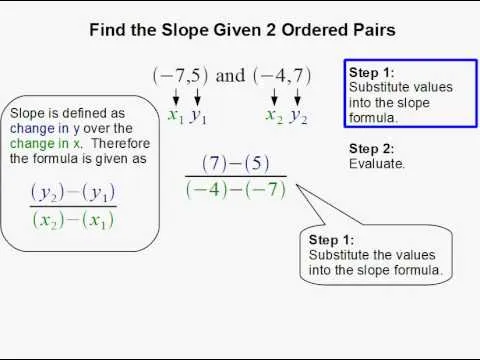











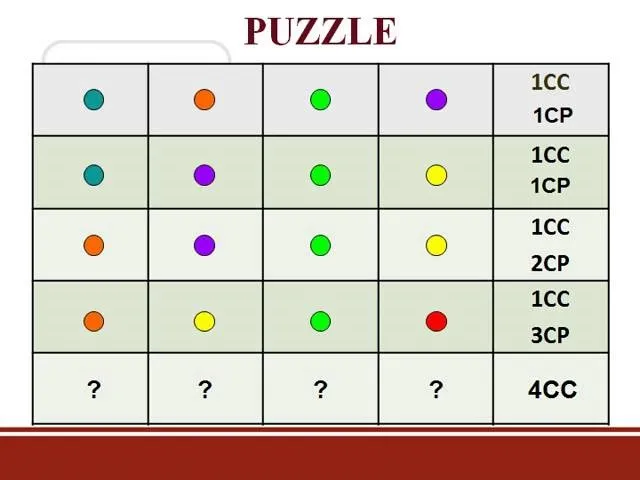




Comments
Be the first, drop a comment!