The discriminate of any equation in any degree plays an important role in determining the roots of that equation. In case of a quadratic equation with a positive discriminate, the roots are real while a 0 discriminate indicates a single real root. A negative discriminant indicates imaginary (complex number format) roots. As shown in the video (along with a plot of the aforesaid equation), the discriminant of the equation a(x^2) + bx + c is (b^2) - 4ac. This is a straightforward way of calculating the discriminant. This same discriminant can be used to even find the roots of the quadratic equation.
Apple's iOS 26 and iPadOS 26 updates are packed with new features, and you can try them before almost everyone else. First, check Gadget Hacks' list of supported iPhone and iPad models, then follow the step-by-step guide to install the iOS/iPadOS 26 beta — no paid developer account required.




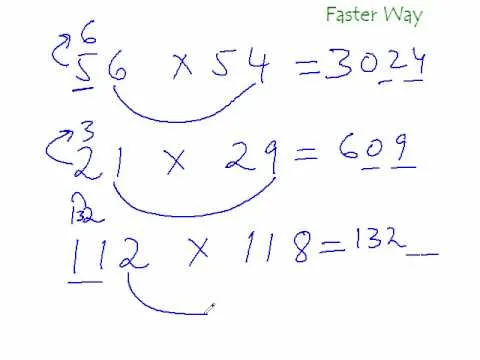
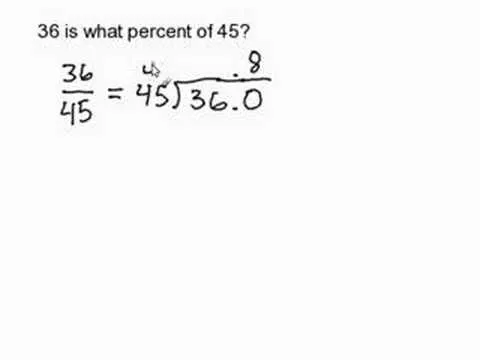
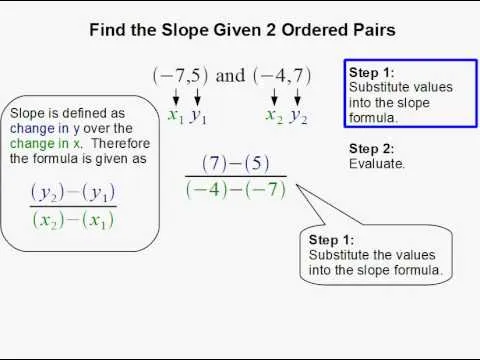











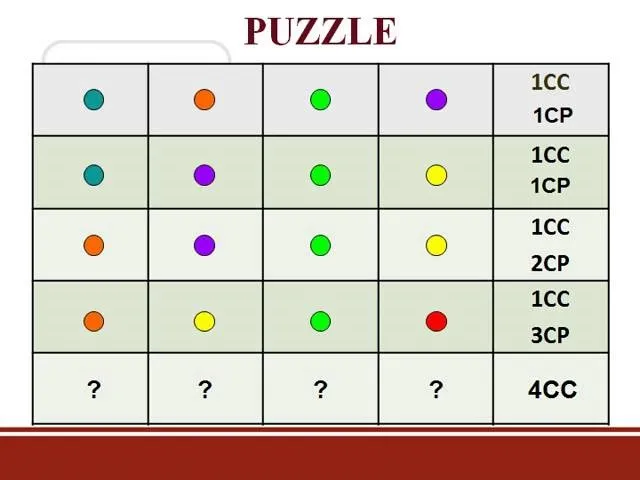




Comments
Be the first, drop a comment!