There wouldn't be any chaos in the world without Benoit Mandelbort— chaos theory, that is. Mandelbrot, who just passed away at the age of 85, pioneered fractal geometry and greatly influenced chaos theory. He spent most of his life working in physics, biology and astronomy, and is best known for his Mandelbrot Set, a mathematical set of points in the complex plane (the boundary of which forms a fractal).
But let's talk about fractal geometry. This video series introduces you to fractals, a topic much enjoyed in mathematics today. Start out by learning about the Sierpinski triangle and move onto Pascal's triangle and iterated functions. These are a great way to introduce yourself to fractal geometry.
The definition of "fractal" is this:
A curve or geometric figure, each part of which has the same statistical character as the whole. Fractals are useful in modeling structures (such as eroded coastlines or snowflakes) in which similar patterns recur at progressively smaller scales, and in describing partly random or chaotic phenomena such as crystal growth, fluid turbulence, and galaxy formation.
Check out the article "Plot the Mandelbrot Set by Hand" on WonderHowTo for more on fractals.





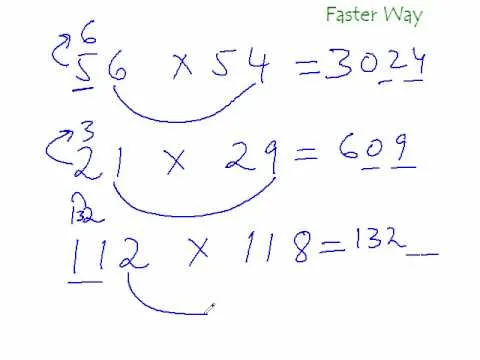
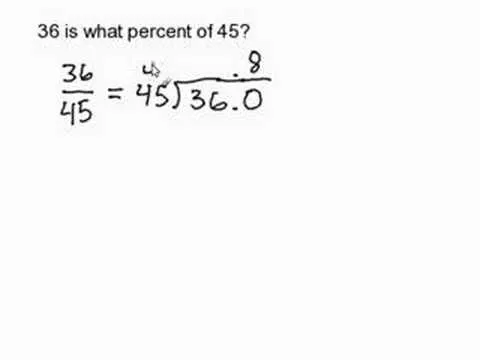
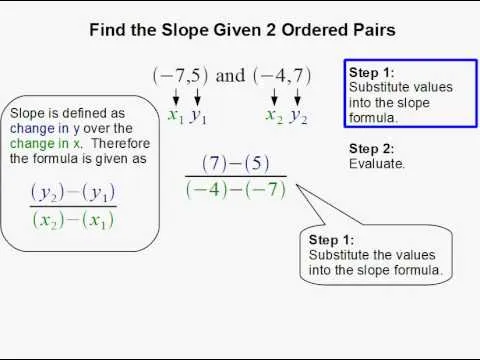











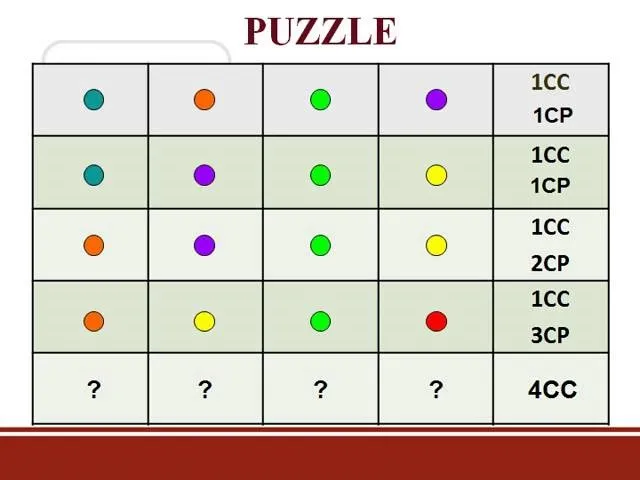




Comments
Be the first, drop a comment!